1. Definition
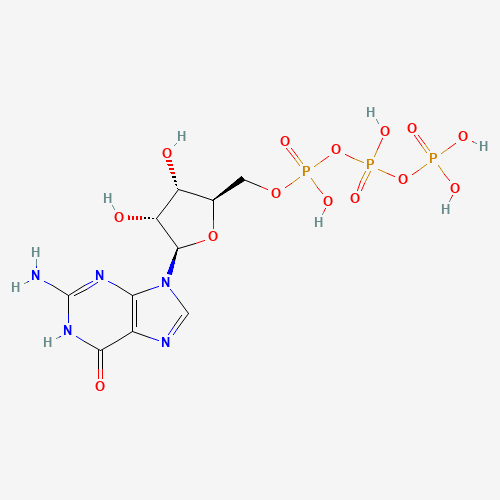
Guanosine triphosphate (GTP) is a chemical compound from the nucleoside triphosphate group. It contains energy-rich phosphate residues and thus serves as an energy store within cells.
2. Chemistry
The GTP molecule is a condensation product of the purine base guanine, the sugar ribose and three molecules of phosphate. Energy is released by splitting off a phosphate residue to form guanosine diphosphate.
Guanosine triphosphate has the molecular formula C10H16N5O14P3 and a molar mass of 523.18 g/mol.
With the help of the enzyme guanylyl cyclase, the signal molecule cGMP can also be synthesized from GTP.
3. Physiology
The released energy can be used in various processes:
1. Signal transduction: GTP activates G-proteins, which transmit signals from cell surface receptors and trigger important cellular reactions such as hormone signaling and sensory stimuli.
2. Recovery of ATP out of ADP
3. Construction of DNA and RNA