1. Definition
Xanthine oxidase (XO) is a metalloenzyme (a hydroxylase) important in the purine metabolism.
2. Structure
The active centre contains two molybdenum atoms and an iron-sulphur cluster. It also contains two FAD molecules. The enzyme occurs as a dimer.
3. Biochemistry
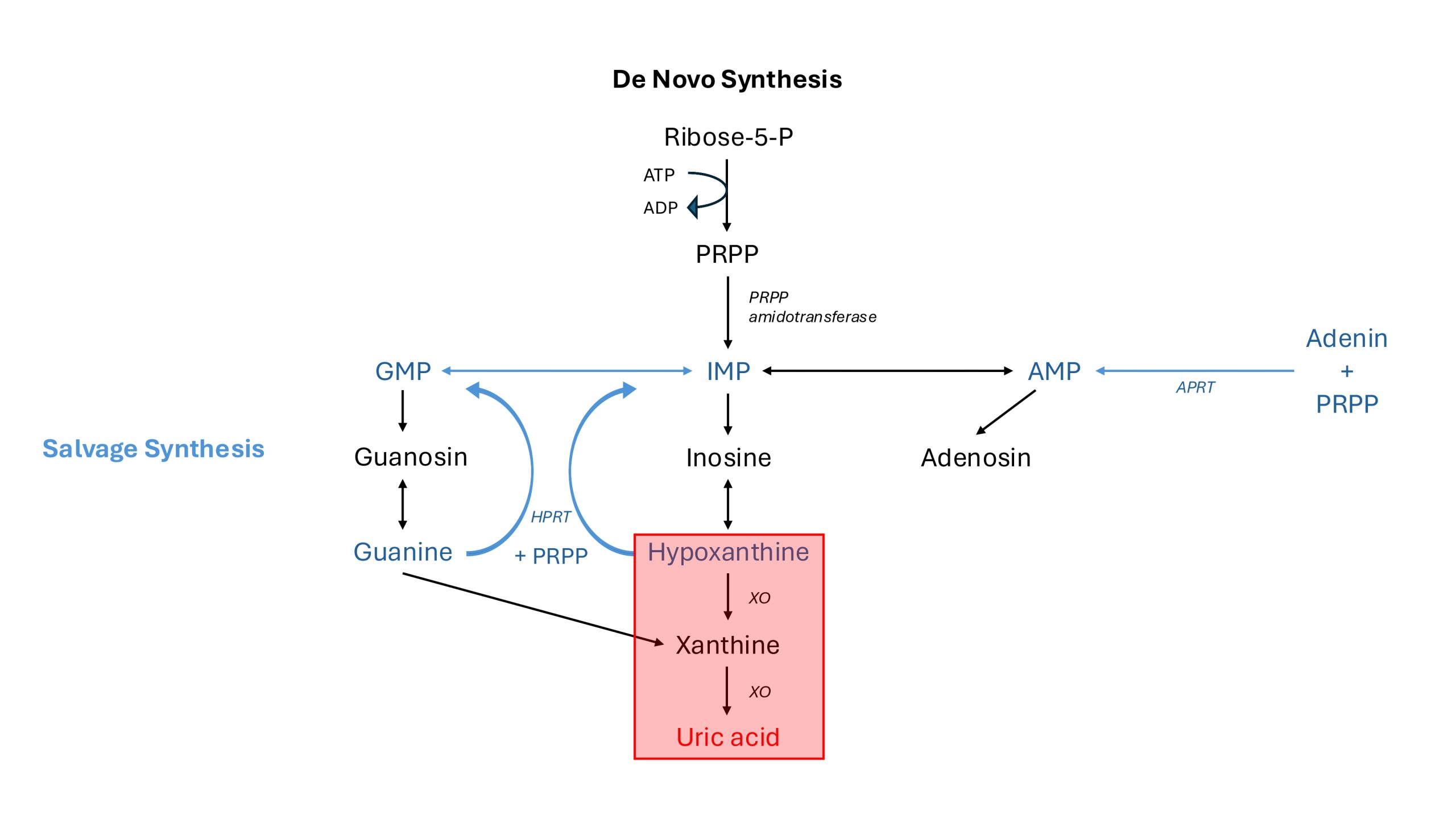
The XO catalyses the oxidation of hypoxanthine and xanthine to uric acid in the kidneys and liver.
- Hypoxanthin + O2 → Xanthin + H2O2
- Xanthin + O2 + 2 H2O → Harnsäure + 2 H2O2
4. Pathology
Hyperuricemia: Increased uric acid formation can be caused by increased activity of liver xanthine oxidase for unexplained reasons.
Xanthinuria: Insufficient conversion of xanthine to uric acid due to low xanthine oxidase activity. The consequence is that Xanthine is excreted in large quantities in the urine.
5. Pharmacology
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors (e.g. Allopurinol or Febuxostat) are administered to prevent the crystallisation of uric acid.
Allopurinol binds firmly to the reduced form of xanthine oxidase and thus inactivates it. This reduces the production of poorly soluble uric acid and increases the concentration of the more soluble compounds xanthine and hypoxanthine.
6. Diagram