1. Definition
Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase, or HGPRT for short, is an enzyme that plays an important role in the metabolism of purine bases.
2. Biochemistry
HGPRT is encoded by the HPRT1 gene.
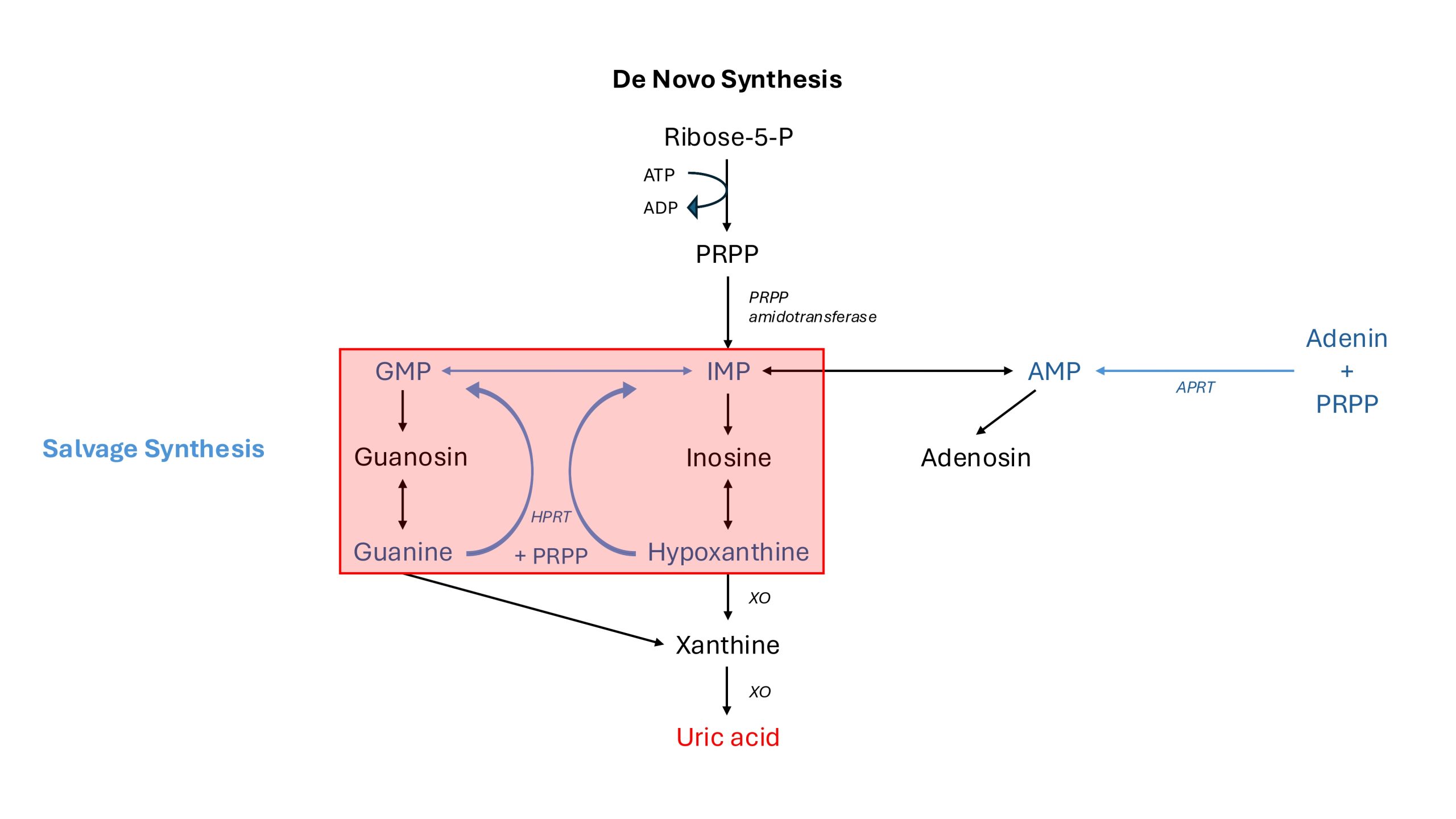
The HGPRT is an essential enzyme for the salvage pathway of the purine metabolism. Here hypoxanthine and guanine are converted into inosine monophosphate (IMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP), respectively, by the enzymatic activity of HPRT, with phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphat (PRPP) serving as a co-substrate.
By enabling the salvage pathway the enzyme increases the energetic efficiency of purine metabolism, as de novo purine nucleotide synthesis can be bypassed via this pathway in order to provide IMP and GMP again.
The importance of this pathway can be recognised by the fact that 90% of purine bases are reused and only 10% are actually degraded and excreted.
3. Pathology
A large number of changes in the HPRT1 gene are known. These are mainly insertions, deletions and point mutations in the gene.
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is a particularly serious metabolic disorder that occurs as a result of a genetic mutation in the HPRT1 gene.
4. Diagram