1. Definition
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms.
2. Background
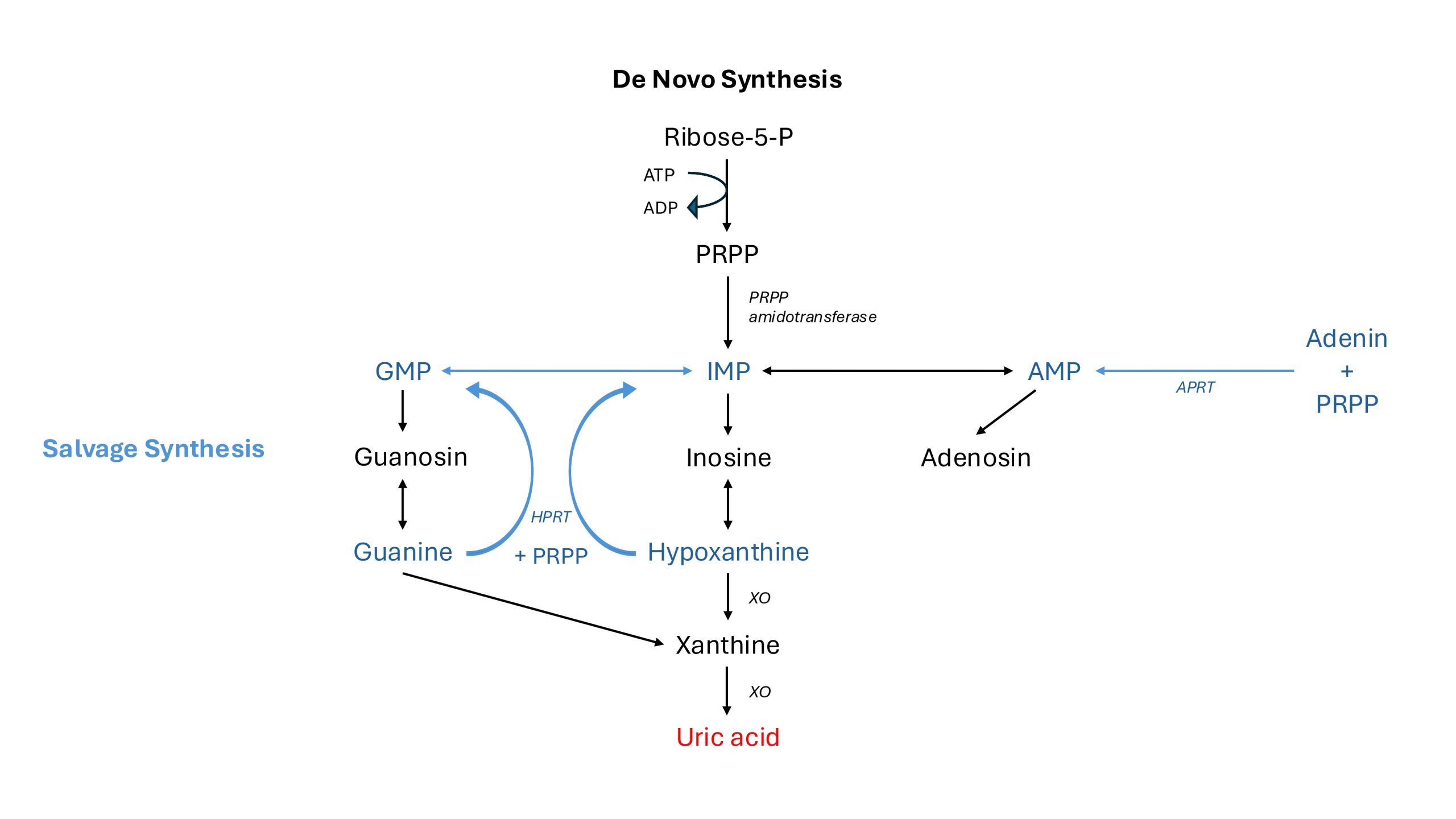
The purine metabolic pathway involves both the salvage and de novo mechanisms. The first step, and the rate-determining reaction in de novo purine biosynthesis, is catalyzed by the 5′-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) amidotransferase enzyme, which enables the conversion of PRPP to the first committed intermediate. The salvage process is primarily enabled by hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) and adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT), which catalyze the conversion of purine bases to their nucleotide equivalents (≙ recycling).
De novo purine biosynthesis is a multi-step, intricate process where four amino acids, one PRPP molecule, two folate derivatives, and three ATP molecules are used to synthesize inosine monophosphate (IMP). In the salvage pathway, hypoxanthine and guanine are converted into inosine monophosphate (IMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP), respectively, by the enzymatic activity of HPRT, with PRPP serving as a co-substrate.
A deficiency of HPRT activity (as seen in LNS) results in the accumulation of its substrates, hypoxanthine and guanine, which are then metabolized to uric acid by xanthine oxidase, with the potential result of hyperuricemia. Moreover, elevated APRT activity may also enhance purine overproduction.
3. Diagram